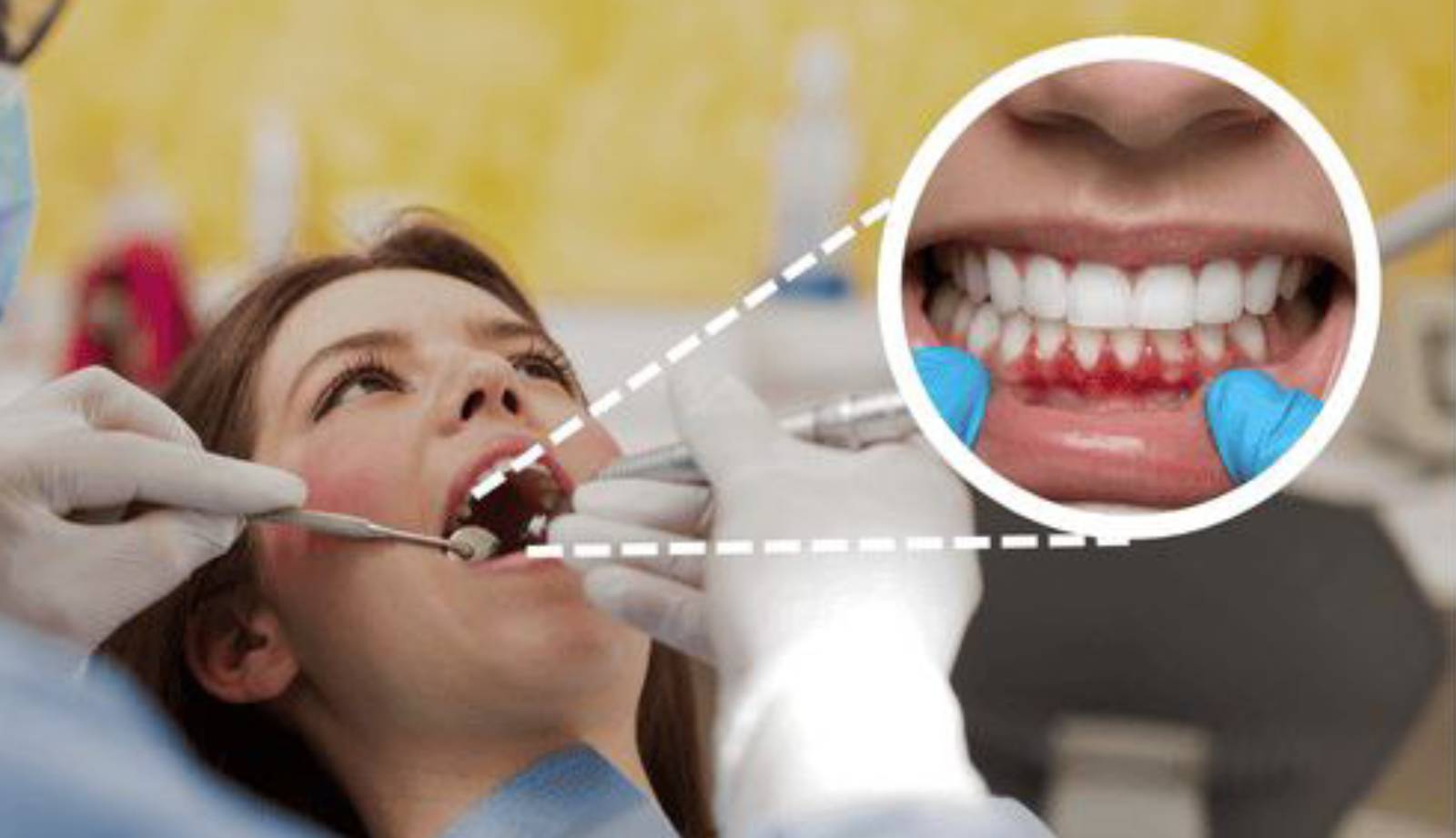
Why Do Gums Bleed? Understanding the Causes and Solutions
Healthy gums are firm, pink, and do not bleed easily. If you notice blood while brushing, flossing, or even eating, it’s a sign that something isn’t right. Bleeding gums are one of the earliest warning signals of gum disease, but they can also be linked to other oral or general health issues. Understanding the reasons behind bleeding gums is the first step toward prevention and effective treatment.
Common Causes of Bleeding Gums-
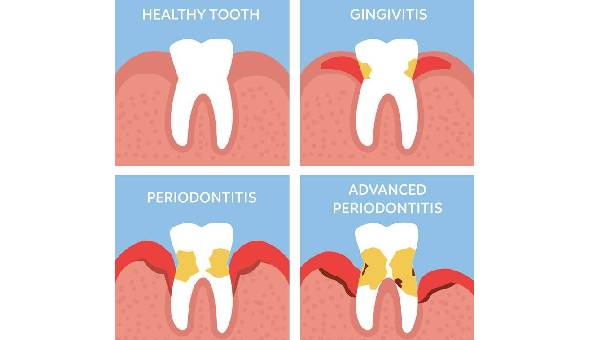
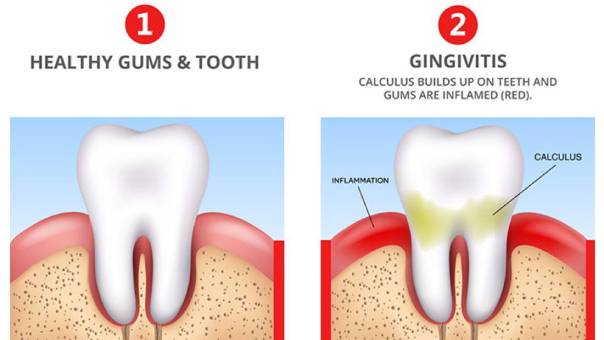
1. Gingivitis (Early Gum Disease)
The most common reason gums bleed is gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease. Poor oral hygiene allows plaque — a sticky film of bacteria — to accumulate on teeth and gums. This irritates the gum tissue, leading to redness, swelling, and bleeding during brushing or flossing. -
2. Poor Brushing or Flossing Technique
Using a hard-bristled toothbrush or brushing too aggressively can damage gum tissues. Similarly, if you have recently started flossing, you may notice some bleeding until your gums adjust. -
3. Periodontitis (Advanced Gum Disease)
If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease. Here, bacteria not only irritate the gums but also attack the bone and supporting structures of teeth, leading to persistent bleeding, gum recession, and potential tooth loss. -
4. Vitamin Deficiencies
Deficiency of vitamins like Vitamin C and Vitamin K can cause gum problems. Vitamin C deficiency weakens gum tissue and blood vessels, while Vitamin K plays a role in clotting — making deficiencies noticeable through gum bleeding. -
5. Medical Conditions and Medications
Systemic health issues such as diabetes, blood clotting disorders, or the use of blood-thinning medications (like aspirin, warfarin) may contribute to gum bleeding. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can also make gums more sensitive.
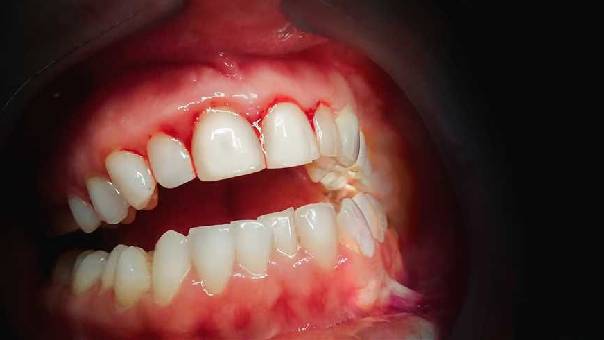
Another lesser-known but important cause of bleeding gums is mouth breathing. People who breathe through their mouth — especially while sleeping — often experience gum irritation and inflammation. This happens because:
-
Dry mouth: Normal saliva flow protects teeth and gums by washing away bacteria and neutralizing acids. Mouth breathing dries out oral tissues, reducing this protection.
-
Plaque buildup: With less saliva, bacteria thrive, leading to plaque accumulation along the gumline.
-
Gum inflammation: Constant exposure to airflow irritates the gingiva, making it red, swollen, and more prone to bleeding.
-
Altered oral pH: Mouth breathing creates an environment favorable to harmful bacteria linked to gum disease.
-
Red, swollen gums (especially in the front teeth region)
-
Bleeding when brushing or flossing
-
Bad breath (halitosis)
-
Shiny, inflamed gum surfaces that appear “dry”
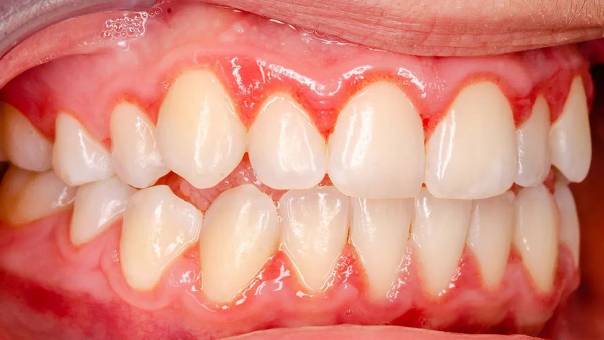
Mouth breathing is particularly common in children who sleep with their mouths open, but it can affect adults as well. Over time, this habit not only worsens gingivitis but also increases the risk of more serious gum disease. Identifying and addressing mouth breathing early — whether through dental evaluation, ENT consultation, or habit correction — can significantly improve gum health.
When Should You Worry About Bleeding Gums?Occasional bleeding from brushing too hard is usually not a major concern. However, consistent bleeding should never be ignored. You should seek dental advice if you experience:
-
Persistent bleeding despite good oral hygiene
-
Swollen, tender, or receding gums
-
Loose teeth or changes in bite
-
Frequent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
These signs often indicate underlying gum disease that requires professional attention.
How to Prevent and Manage Bleeding Gums-
1. Maintain Proper Oral Hygiene
-
Brush twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush
-
Floss at least once a day to remove plaque between teeth
-
Use an antimicrobial mouthwash if recommended by your dentist
-
-
2. Regular Dental Check-ups
Professional cleaning helps remove tartar and detect gum problems early. -
3. Balanced Nutrition
Eat a diet rich in Vitamin C (fruits, vegetables) and Vitamin K (leafy greens) to support gum health. -
4. Stay Hydrated
Drinking water helps maintain saliva flow, especially important if you are prone to mouth breathing. -
5. Address Mouth Breathing
If you or your child breathe through the mouth frequently, consult a dentist or ENT specialist to identify and correct the cause. -
6. Manage Systemic Health Conditions
Keep conditions like diabetes under control and inform your dentist about medications you take.
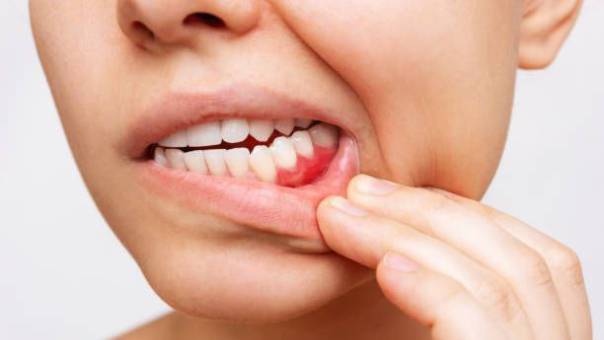
Bleeding gums are more than just a minor inconvenience — they are a warning sign that your oral health needs attention. Whether caused by poor oral hygiene, vitamin deficiencies, medical conditions, or habits like mouth breathing, the good news is that gum bleeding can usually be treated and prevented with timely care.
At Trivandrum Dental Specialists’ Group, we combine expert diagnosis with advanced treatments to restore gum health and protect your smile.
Don’t ignore bleeding gums. Book your consultation today and take the first step toward healthy gums and a confident smile.